b dna and z dna difference|Different forms of DNA : Cebu The information from the base composition of DNA, the knowledge of dinucleotide structure, and the insight that the X‐ray crystallography suggested a . Tingnan ang higit pa bet365 - La empresa de apuestas deportivas en línea más popular del mundo. El servicio en directo más completo. Vea Deportes en directo. 'Imágenes en directo' disponibles en el PC, dispositivo móvil y tableta. Apueste en Deportes. Apueste en Deportes ahora, incluido fútbol, tenis y baloncesto.
b dna and z dna difference,B-form DNA. Dimensions of B-form (the most common) of DNA; Major and minor groove; A‑form nucleic acids and Z‑DNA. Differences between A-form and B-form nucleic acid; Z-form DNA; Three major forms of DNA are double stranded and connected by interactions between . Tingnan ang higit paThe information from the base composition of DNA, the knowledge of dinucleotide structure, and the insight that the X‐ray crystallography suggested a . Tingnan ang higit paThree different forms of duplex nucleic acid have been described. The most common form, present in most DNA at neutral pH and physiological salt . Tingnan ang higit paZ-DNA is a radically different duplex structure, with the two strands coiling in left-handed helices and a pronounced zig-zag (hence the name) pattern . Tingnan ang higit paThe key difference between form B DNA and Z DNA is that the B-DNA is right-handed, while the Z-DNA is left-handed. B DNA. Commonly occurring DNA form in normal physiological conditions, this form of DNA . Z-DNA can form when the DNA is in an alternating purine-pyrimidine sequence such as GCGCGC, and indeed the G and C .
(1). A-DNA (2). B-DNA (3). Z-DNA. Among these three types, the most abundant type of DNA is B-DNA, commonly known as Watson . For instance, a protein could bind both B-DNA and Z-DNA under different conditions. This outcome would be analogous to that seen for the telomere binding Rap1 .
B-DNA is the standard form found in most organisms, while Z-DNA is typically found in regions of DNA with high GC content or under certain conditions such as high salt .b dna and z dna differenceAmong six different forms of DNA, B, A and Z forms are the most common: B-form. It is the most common form of DNA, which exists as a right-handed double-helical DNA. It was pioneered by Watson and Crick. B-DNA .
B-DNA and Z-DNA are two of the three conformations of DNA that occur in nature. Moreover, the diameter of B-DNA is 20 Å, and it contains 10 residues per turn while the diameter of Z-DNA is 18 Å, and it .

Nucleic Acids. Nucleus. Physiological Probes. B-DNA and Z-DNA are two of three common DNA conformations. There are several significant differences between the .
Introduction. The main backbone of the human genome is comprised of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) in the canonical B-DNA conformation with a right .
The differences in photochemical reactivity of TA dinucleotides with psoralen (reactive in double-stranded DNA but not in single-stranded DNA or in the junctions between the B- and Z-DNA regions) were used to . The properties of six commonly used, commercially available, fluorescent dyes were compared in staining right-handed B-DNA and left-handed Z-DNA. All showed different degree of fluorescence turn-on in the presence of B-DNA, but very little in the presence of Z-DNA. The optimal range of dye-DNA ratios of DNA was determined. While .Different forms of DNA Recent advances in DNA synthesis methods have made it possible to carry out single-crystal x-ray analyses of double-stranded DNA molecules of predetermined sequence, with 4 to 12 base pairs. At least one example has been examined from each of the three known families of DNA helix: A, B, and Z. Each family has its own intrinsic . Each time a DNA segment turns into Z-DNA, two B–Z junctions form. These have been examined extensively 10, 11, 12, but their structure was unknown. Here we describe the structure of a B–Z . The similarities between DNA and RNA in the Z-conformation come in contrast to the native states of the two nucleic acids, adopting the B- and A- conformation, respectively ( Figure 1 ). Z-conformation nucleic acids adopt a narrower, more elongated double helix with helical rise and diameter of 44.6 Å and 18 Å, respectively, in contrast to .
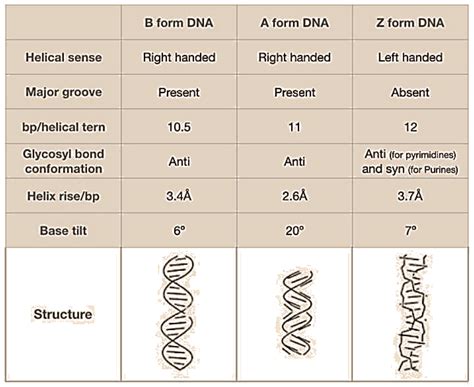
# Helical turns की Height B DNA में 34Å और Z DNA में 44Å होती है. # B DNA में Number of base pairs per helical turn 10 और Z DNA में 12 होते हैं. # B DNA में हर base pair के बीच Distance 3.4 Å और Z DNA में 7.4 Å होती है.Left-handed Z-helices. Biology of A-, B-and Z-DNA. Summary. Acknowledgements Figure 1 Different views of the DNA helix. (a) The structure of B-DNA as proposed by Watson and Crick in 1953, based on fibre diffraction studies. ModifiedfromSindenetal.(1998).(b)A-,B-andZ-DNA,asseenfromthesideofthehelix(above),andlookingdownthehelixaxis(below .b dna and z dna difference Different forms of DNA There are three major families of DNA helices: A-DNA, B-DNA and Z-DNA. The helical. structure of DNA is variable and depends on the sequence as well as the environment. Introduction. Pictures of . The tertiary structure determines the overall structural form of. DNA, most predomin ant examples being B-form, A-form and Z-form. There are four variables by which. DNA structure may differ . B-DNA तथा Z- DNA में अंतर | Difference Between B-DNA And Z-DNA | B-DNA aur Z-DNA mein antar class 12 #biologysciencesk #biologyclass12 @BiologyScienceSK13
Despite all the investigations about the biological role of left-handed Z-DNA, the microscopics behind the B–Z-DNA transition have remained controversial, with several different mechanisms proposed in the literature ().Generally speaking, the models for the B–Z transition are classified into mechanisms that involve either base pair opening or .The Z-DNA structure. Proteopedia Z-DNA. Z-DNA is one of the many possible double helical structures of DNA.It is a left-handed double helical structure in which the helix winds to the left in a zigzag pattern, instead of to the right, like the more common B-DNA form. Z-DNA is thought to be one of three biologically active double-helical structures along with .There are three different DNA types: A-DNA: It is a right-handed double helix similar to the B-DNA form. Dehydrated DNA takes an A form that protects the DNA during extreme conditions such as desiccation. Protein binding also removes the solvent from DNA, and the DNA takes an A form.DNA is the fundamental genetic component of multicellular organisms composed of nucleotide bases, phosphate groups, and ribose sugar. It can attain different forms based on salt concentration, hydrogen level, altered bases, etc. Those forms are named A-DNA, B-DNA and Z-DNA. The calculated free energy difference between B- and Z-DNA is 21.6 kcal/mol and between methylated B- and Z-DNA is 14.4 kcal/mol. A recent targeted molecular dynamics study of a B-Z junction has reported a barrier of 13 kcal/mol and a free energy difference of 4.7 kcal/mol for a 10 base pair DNA sequence, .

Pergunta de Cláudio Márcio Almeida em 31-05-2022. (9 votos) A forma Z - DNA apresenta seu sentido de rotação para a esquerda. Esta conformação é mais alongada e mais fina do que o B - DNA. Para completar uma volta na hélice são necessários 12 pares de bases. O DNA, em solução com altas concentrações de .
Recent advances in DNA synthesis methods have made it possible to carry out single-crystal x-ray analyses of double-stranded DNA molecules of predetermined sequence, with 4 to 12 base pairs. At least one example has been examined from each of the three known families of DNA helix: A, B, and Z. Each family has its own intrinsic restrictions on . An important non-canonical structure associated with Z-DNA is a BZ junction that forms where B-DNA and Z-DNA meet with an extrusion of bases at the junction between the B- and Z-DNA (Ha et al. 2005; Subramani et al. 2019).Accordingly, when Z-DNA forms in the genome, two BZ junctions flank each side of the Z-DNA-forming site .
b dna and z dna difference|Different forms of DNA
PH0 · Z
PH1 · What is the Difference Between B DNA and Z DNA
PH2 · What are the differences between B
PH3 · Special Issue: A, B and Z: The Structure, Function and Genetics
PH4 · Different forms of DNA
PH5 · Different Forms of DNA
PH6 · Difference between B DNA and Z DNA
PH7 · Difference between A
PH8 · B DNA vs. Z
PH9 · 2.5: B